Epigenetic changes may be involved in Covid19 and LongCovid, which might be able to be changed back with the addition of plenty of methyl donor vitamins. People with methylation genetic alleles would be more at risk for epigenetic changes to DNA or actin protein filaments. Actin are semi flexible proteins in a double helix shape which support the fluid and organelles inside of cells and around cells and organs of our bodies. Actin also is involved in guiding the work of DNA replication and growth and development of cells or infants.
Methylation is the addition of a methyl group – one carbon atom and three hydrogen atoms, to genes, or actin filaments. A methylated gene is not active for encoding proteins while a demethylated gene is available to be transcribed into a messenger mRNA to be made into a matching protein. Actin filaments are a double helix shape like DNA but do other functions throughout our body. Some have methyl groups also that seem to be essential for proper function of the actin protein whether in muscle contraction or in guiding chemicals within cells to make DNA or do other work. Actin filaments add structure to the jelly like fluid around and in cells and may tether chemicals in place for chemical reactions or guide cellular organization during growth and development.
Actin may be involved with energy fields of our body along with microtubules also, but that is not discussed in greater detail in this post (more information about quantum energy fields and actin is included in Cracking Nature’s Code (2019) (1), and in several posts on another site of mine first in the series, 2nd, 3rd, 4th).
Viral infection and epigenetic changes with a focus on Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome and possible dietary and lifestyle changes that may help reverse epigenetic changes is the focus of this post – which got long. It is also available as a section of this document that includes the series on Mast Cells and Histamine. Current standard of treatment for patients with POTS symptoms may leave them unwell for years – a few get better more rapidly. I got better on my own within a few months – twice. More about possible strategies for improvement of epigenetic changes will be included later in the post. More about the epigenetics involved in POTS is included in the Genetics/Epigenetics chapter of my book draft which is available on a platform where you can get an e-copy early (minimum price Free, Leanpub/Tipping The Clock Toward Health) and then be informed of updates with an email subscription.
Viral infection can cause Epigenetic changes.
“Bacterial (Pacis et al., 2015, 2) and viral infection (Lichinchi et al., 2016, 3) directly impact methylation patterns, most likely orchestrated by actin since it is universally hi-jacked in viral infectivity (Cudmore et al. 1997, 4; Ohkawa and Volkman, 1999, 5; Lu et al., 2004, 6; Marek et al., 2011, 7).”
page 34, JB Head, PhD, Cracking Nature’s Code (2019) (1)
I found I have methylation gene alleles in a genetic screening (post: Methylation Cycle Defects – in me – genetic screening “for research purposes only”). Since finding out I stopped taking standard supplements of B12 and folic acid because they are not methylated, not bioactive. I take methyl B12 & methyl folate supplements now. Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS) (9) has been a problem for me in past years a couple times and I got better. Symptoms include a rapid heart rate, tachycardia, and feeling faint or blacking out, especially when getting up quickly from a seated or laying down position to standing. (9) I have heard anecdotal reports of it being a symptom for some LongCovid survivors who had never had the problem before.
To slow the rapid heart rate during an episode I found it helpful to stop and sit or lay down with my feet above my heart if possible and just wait a couple minutes for the rapid heart rate to slow again. Continuing to exercise would make the rapid heart rate worse. Preventing the faintness upon rapidly getting up required trying to remember to slow down and have a support ready to hold if I felt wobbly. I did faint once, odd to find yourself on the floor unexpectedly.
POTS has been found to potentially involve a genetic difference in the norepinephrine transporter gene (SLC6A2) sequence and it can also be an epigenetic problem with links to excess formaldehyde. (9) Formaldehyde can donate methyl groups to DNA that normally would be unmethylated – active. (10) Methylation of DNA is a little like a on/off switch for genes, or the cap on bottle – add the methyl groups and the DNA gene is inactive.
“Formaldehyde as a methyl donor for the methylation of DNA, RNA, and histone acts as an epigenetic factor participating in the reversible and dynamic methylation. DNA demethylation elicits formaldehyde generation in the dividing cells and post-mitotic neurons.” (10) Memory formation involves methylation of DNA and cognitive impairment in older adults is associated with increased internal formaldehyde levels (self-made) and demethylation of DNA. Use of nutrients to remove formaldehyde helped improve memory in an animal based study. (10)
Formaldehyde can be prevalent in secondhand or thirdhand smoke in enclosed rooms, or smog, or we make our own during normal metabolism, and physical or emotional stress conditions may cause an increase, as well as the level potentially increasing in older adults. (11) Elevated levels of formaldehyde within cells causes more breakdown of sugar for energy and increased removal of an antioxidant out of the brain cells, which may increase risk for cognitive damage. “As excess formaldehyde accelerates glycolysis and glutathione export in neural cells, formaldehyde‐induced alterations in brain metabolism and oxidative stress may contribute to the pathological progression of neurodegenerative disorders.” (11)
Formaldehyde is very reactive and can use the methyl group to form links between protein groups or parts that wouldn’t normally be linked – like bungee cords holding parts together in places that would be separate in normal function. (11) Formaldehyde is used with tissue samples to preserve material for viewing under a microscope. Studies of the effect of formaldehyde on the actin protein of live cells that were low on blood sugar found that modifications to the protein did occur – the authors suggest any prior research on the actin protein in formaldehyde treated samples may be inaccurate. (12) Take home point – formaldehyde is not good for our brain cells and may effect the protein of our brain cytoskeleton structure. (12) Protein tangles in brain cells are associated with dementia and autism.
What is a cytoskeleton? We are mostly water, so how do we walk around? With a balance in tension between string like ligaments and muscles and rod like bones of our skeleton. Within the cellular environment, inside and outside the cell membrane – the tent wall, there are rod like microtubules and string like actin protein that is more flexible, it can change shape but isn’t stretchy as much as structurally able to modify in shape. Actin is a double helix, two spirals like DNA except without the ladder like steps joining the two lengths of protein. When force is applied the double helix can get a little longer or shorter as the coils compress or lengthen slightly – tensile strength – and the protein gets stiffer from a side to side direction – torsion – and is less flexible along the length, less able to bend sideways. (13)
The actin protein may act as torsion sensors – is the environment changing in pressure around that section of the protein length – from increased fluid or gas? How full is the balloon like membrane? (14) Channels in a membrane will open and start to leak rather than letting the membrane burst like an overfull balloon. This may seem like a silly discussion – however it is your brain and organs – leaking is better than bursting. Leaking membranes will release fluid and some types of chemicals while a bursting open, as when viral replication is complete and the virus exit a cell, the membrane bursts and all the remaining chemicals in the cell flood into the surrounding cytoskeleton and can cause inflammatory damage to surrounding cells.
These flexible yet firm cytoskeleton actin filaments also may act like guidelines for directing traffic or tethering organelles in place for activity such as replication of DNA during cell division (one cell doubles its DNA and then divides into two cells). Too much of the proteins within a cell nucleus will prevent DNA replication rather than guiding it. (15) Actin is also involved in muscle fiber motion. The double helix structure can also be methylated with methyl groups doing an unknown but critical function. Loss of methylation of actin in one location is associated with cancer and autism spectrum disorders, (16), loss of it in another location along the protein chain is associated with muscle changes that cause female animals to have delivery problems and fewer babies. (17, 18)
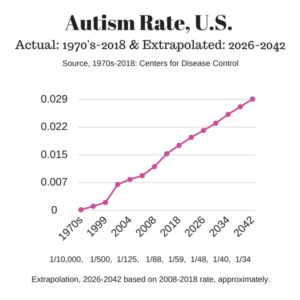
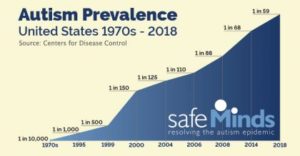
So actin is important stringy protein that effects muscle power, cell division, and the brain – and formaldehyde can cause demethylation of DNA, likely it can cause demethylation of actin also which may lead to autism spectrum disorders, cancer, and muscle problems that can affect a healthy delivery of infants (in an animal study). The visual – we want our jelly like insides to have a strong yet flexible tent membrane, tent poles (microtubules), and tie downs (actin) – without having so many tie downs it starts looking like a haunted house full of cobwebs. The amyloid beta protein associated with Alzheimer’s dementia and autism may be protective against a low level infection (post: Magnesium might help protect against beta amyloid placques) but also may increase changes in actin stress fibers (24) and an excess seems to add to chronic inflammatory damage over time.
How do we achieve this? Healthy actin?
It may help promote appropriate methylation of DNA and actin to have adequate antioxidants and methyl donor nutrients in our diet, to reduce oxidative stress chemicals and provide adequate methylation to DNA and actin. Avoiding excessive physical and emotional stress may also be an important strategy, so we aren’t embalming ourselves with self produced formaldehyde (the mummy in the haunted house being our own brain).
We also want to avoid formaldehyde in our environment, which would include improving air quality, especially during sleep hours when our body is focused on detoxification of the brain. Parkinson’s Disease is another chronic condition that may involve epigenetic changes and reducing formaldehyde exposure may be protective. More information is in this post with a link to a longer post about formaldehyde sources: The Cholinergic System
Increasing methyl donor vitamin rich foods and/or supplements should focus on the methylated form if unsure whether there is a genetic allele problem causing lack of methylation.
- Fortified breakfast cereal and other fortified foods would have the unmethylated form of folate – folic acid. Peas, asparagus, orange juice with the pulp would have the natural methylated folate. See: Folate is essential and Folic Acid is commonly available.
- The B vitamin methyl donors also include methyl B12, Vitamin B12 deficiency can cause long term nerve degeneration, and betaine and choline.
- BPA is an environmental toxin that takes methyl groups. See this post for more information about food sources of methyl donor nutrients and tips for avoiding BPA. Methyl Donors and BPA, or B vitamin methyl donors may help protect against risks from BPA
- The amino acid methionine (8) is also a methyl donor nutrient. Glyphosate may reduce methionine availability. Glyphosate and COVID-19
“Methyl groups are important for numerous cellular functions such as DNA methylation, phosphatidylcholine synthesis, and protein synthesis. The methyl group can directly be delivered by dietary methyl donors, including methionine, folate, betaine, and choline.” … “Studies that simulated methyl-deficient diets reported disturbances in energy metabolism and protein synthesis in the liver, fatty liver, or muscle disorders.” … “Hypomethylation has a wide spectrum of effects that include genetic, epigenetic, and metabolic alterations.” (8)
Gastrointestinal problems have been found to be common among patients with Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS) with malfunction or slowing, dysmotility, of the smooth muscle lining of the intestinal tract. “Case study 1: A 20-year-old woman presented to clinic for further evaluation of a several year history of fullness and epigastric discomfort associated with eating and irregular bowel habits. Her weight was stable. She also described frequent migraine headaches, episodic palpitations and lightheadedness with progressively increasing episodes of syncope. A systems review was notable for profound fatigue, dry eyes and mouth and intermittent flushing and pruritus.” (19) The patient’s symptoms include many in common with Mast Cell Activation Syndrome, however testing for mast cell activation was normal. Patients whose symptoms followed a viral infection tend to get better more often than patients with a family history of POTS. (19)
“A number of chronic conditions are frequently seen in patients with POTS and contribute to symptom burden and reduced quality of life. Common comorbidities include chronic fatigue syndrome, fibromyalgia, interstitial cystitis, and migraine headaches. Other unique conditions that seem to occur with increased frequency in POTS are autoimmunity, the hypermobile form of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (HM-EDS), and mast cell activation disorder (MCAD).” (19)
“Unlike mastocytosis, idiopathic mast cell activation [MCAD] occurs in the absence of mast cell proliferation and with episodic accumulation of mast cell mediators in the plasma or urine, usually present when symptomatic. Patients with MCAD typically present with episodic “attacks” of flushing, urticaria and pruritus accompanied by lightheadedness, dizziness, dyspnea, nausea, headache, diarrhea, and/or syncope; symptoms representative of the hyperadrenergic type of POTS with biochemical evidence of MCAD (20).” (19)
The patient in case study 2 had ongoing nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and weight loss continuing for years following a viral infection. She was found to have deficiency in iron, zinc, and vitamin B12 and gastroparesis (slow or little intestinal muscle action). Intravenous iron and B12 were provided and an oral zinc supplement. Nutrient levels improved however the GI symptoms and weight loss continued and the patient was given tube feedings which improved weight, however some intolerance to the tube feedings continued and abdominal pain persisted. (19)
If demethylation of actin protein in the muscle tissue of the intestinal wall was a problem for the patient in case study 2, then it may have been a factor in the gastroparesis. Genetic screening for methylation defects is not mentioned. Supplements of B12 are often an unmethylated form, cyanocobalamin, and which include cyanide. (21) In a study of 12 patients by Huang et al, (22): “Disturbances in GI motility were found to involve not only the stomach, but also multiple segments of the gut spanning the esophagus to the anus.” (19) The commonly used treatments for GI symptoms associated with POTS (see Table 5) do not include nutrients and do include proton pump inhibitors, (19), a medication that takes the place of magnesium as a calcium channel blocker, and which may lead to worse magnesium deficiency for some people, a genetic difference may be involved. See post: Original Prilosec Warning, edited.
Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) may occur along with GI problems and lead to fat and carbohydrate digestion and absorption problems and bloating from excessive bacterial growth. Changes in diet due to the discomfort are common in patients with POTS and these more severe GI symptoms and which may lead to deficiencies in fat soluble vitamins A, D, E and K. Megaloblastic anemia may result from deficiencies in iron, folate and vitamin B12. (19) Sulfate deficiency may be an underlying factor (23) and providing Epsom salt soaks of the lower legs and feet, or in a bath one to two times a week might help by providing a topically absorbed form of magnesium and sulfate. See post: To have optimal Magnesium needs Protein and Phospholipids too.
Zinc is also involved in DNA methylation and deficiency of the trace mineral can lead to epigenetic changes and gene transcription problems. Zinc is needed along with actin and other proteins to tell the cell nucleus and cell which genes to make into mRNA to be encoded into a protein. “Accumulating evidence has demonstrated that several key enzymes and zinc finger proteins with zinc atom(s) in the reactive center and binding site play important roles in DNA methylation and histone modifications. Therefore, zinc deficiency may disrupt the functions of these enzymes and proteins and result in epigenetic dysregulation. Furthermore, zinc deficiency may enhance inflammatory response and subsequently alter DNA methylation status of the genes involved in inflammation.” (20) Also see posts: Zinc – big news, CoV and other illness related, and Zinc, cancer, and bitter taste receptors.
Disclaimer: Opinions are my own and the information is provided for educational purposes within the guidelines of fair use. While I am a Registered Dietitian this information is not intended to provide individual health guidance. Please see a health professional for individual health care purposes.
Reference List
- JB Head, PhD, Cracking Nature’s Code: The Potential Answer to Everything. (Balboa Press, Bloomington, IN, 2019) https://www.balboapress.com/en/bookstore/bookdetails/792280-cracking-natures-code
- Pacis A, Tailleux L, Morin AM, et al., Bacterial infection remodels the DNA methylation landscape of human dendritic cells. Genome Res 2015. 25: 1801-1811 https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.192005.115 https://genome.cshlp.org/content/25/12/1801
- Lichinchi G, Zhao BS, Wu Y, et al. Dynamics of Human and Viral RNA Methylation during Zika Virus Infection. Cell Host Microbe. 2016;20(5):666-673. doi:10.1016/j.chom.2016.10.002 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5155635/
- Cudmore S, Reckmann I, Way M. (1997). Viral manipulations of the actin cytoskeleton. Trends in microbiology. 5. 142-8. 10.1016/S0966-842X(97)01011-1. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/14077627_Viral_manipulations_of_the_actin_cytoskeleton
- Ohkawa T, Volkman LE, Nuclear F-Actin Is Required for AcMNPV Nucleocapsid Morphogenesis, Virology, Vol 264, Issue 1, 1999, Pages 1-4, ISSN 0042-6822, https://doi.org/10.1006/viro.1999.0008. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0042682299900089
- Lu, S., Ge, G. & Qi, Y. Ha-VP39 binding to actin and the influence of F-actin on assembly of progeny virions. Arch Virol149, 2187–2198 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-004-0361-4 https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00705-004-0361-4
- Marek M, Merten OW, Galibert L, Vlak JM, van Oers MM. Baculovirus VP80 protein and the F-actin cytoskeleton interact and connect the viral replication factory with the nuclear periphery. J Virol. 2011;85(11):5350-5362. doi:10.1128/JVI.00035-11 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3094977/
- Obeid R. The metabolic burden of methyl donor deficiency with focus on the betaine homocysteine methyltransferase pathway. Nutrients. 2013;5(9):3481-3495. Published 2013 Sep 9. doi:10.3390/nu5093481 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3798916/
- Richard Bayles, Harikrishnan KN, Elisabeth Lambert, et al., Epigenetic Modification of the Norepinephrine Transporter Gene in Postural Tachycardia Syndrome. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology. 2012;32:1910–1916 https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.111.244343 https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/atvbaha.111.244343
- Su, Tao & He, Rong-Qiao. (2017). Formaldehyde Playing a Role in (De)methylation for Memory. 10.1007/978-94-024-1177-5_3. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/320523716_Formaldehyde_Playing_a_Role_in_Demethylation_for_Memory
- Ketki Tulpule Ralf Dringen, Formaldehyde in brain: an overlooked player in neurodegeneration?, J. Neurochem. (2013) 127, 7– 21 https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/jnc.12356
- Vasicova P, Rinnerthaler M, Haskova D, et al. Formaldehyde fixation is detrimental to actin cables in glucose-depleted S. cerevisiae cells. Microb Cell. 2016;3(5):206-214. Published 2016 Apr 12. doi:10.15698/mic2016.05.499 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5349148/
- Effect of tensile force on the mechanical behavior of actin filaments. J Biomechanics (2011), 44(9): 1776-1781, 2011-06-03 , https://repository.kulib.kyoto-u.ac.jp/dspace/handle/2433/152437 https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/39280196.pdf
- Hayakawa K, Tatsumi H, Sokabe M. Actin filaments function as a tension sensor by tension-dependent binding of cofilin to the filament. J Cell Biol. 2011;195(5):721-727. doi:10.1083/jcb.201102039 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3257564/
- Hu, X., Liu, Z.Z., Chen, X. et al. MKL1-actin pathway restricts chromatin accessibility and prevents mature pluripotency activation. Nat Commun10, 1695 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09636-6 https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-019-09636-6
- Seervai RNH, Jangid RK, Karki M, et al., The Huntingtin-interacting protein SETD2/HYPB is an actin lysine methyltransferase. Science Advances, 02 OCT 2020 : EABB7854 SETD2 regulates actin dynamics and cell migration via methylation of actin at Lys68 in a cellular complex containing Huntingtin. https://advances.sciencemag.org/content/6/40/eabb7854? “Disruption of the SETD2-HTT-HIP1R axis inhibits actin methylation, causes defects in actin polymerization, and impairs cell migration. Together, these data identify SETD2 as a previously unknown HTT effector regulating methylation and polymerization of actin filaments and provide new avenues for understanding how defects in SETD2 and HTT drive disease via aberrant cytoskeletal methylation.“… “Loss of SETD2 and the H3K36me3 chromatin mark is embryonic lethal in Drosophila (7) and mice (8), and SETD2 defects have been linked to several diseases, including cancer (9–11) and autism spectrum disorder (12–14).”
- Wilkinson, A.W., Diep, J., Dai, S. et al. SETD3 is an actin histidine methyltransferase that prevents primary dystocia. Nature 565, 372–376 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0821-8, https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-018-0821-8 lack of the methylation at histidine 73 seems to interfere with muscles and causes the genetically different animals to have fewer babies due to maternal delivery problems. Graphic from the article shows a CH3 methyl group being added to an actin filament at Histidine 73: https://twitter.com/anandb4/status/1073255833813671937?s=20
- Kwiatkowski S, Seliga AK, Veiga-da-Cunha M, et al., SETD3 protein is the actin-specific histidine N-methyltransferase. bioRxiv 266882; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/266882Now published in eLife doi: 10.7554/elife.37921 https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/266882v1?platform=hootsuite “Finally, Setd3-deficient HAP1 cells were devoid of methylated H73 in β-actin and exhibited phenotypic changes, including a decrease in F-actin content and an increased glycolytic activity. “
- DiBaise JK, Lunsford TN, Harris LA, Nutrition Issues in Gastroenterology, Series #187: The POTS (Postural Tachycardia Syndrome) Epidemic: Hydration and Nutrition Issues. June 2019, Practical Gastro, Vol XLIII, Issue 6 https://practicalgastro.com/2019/10/14/the-pots-postural-tachycardia-syndrome-epidemic-hydration-and-nutrition-issues/
- Gu H.F., Zhang X. (2017) Zinc Deficiency and Epigenetics. In: Preedy V., Patel V. (eds) Handbook of Famine, Starvation, and Nutrient Deprivation. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-40007-5_80-1 https://link.springer.com/referenceworkentry/10.1007%2F978-3-319-40007-5_80-1
- Dody Chiropractic, Why Do Vitamin B12 Supplements Contain Cyanide?, dodychiro.com, https://www.dodychiro.com/why-do-vitamin-b12-supplements-contain-cyanide/
- Huang RJ, Chun CL, Friday K, et al. Manometric abnormalities in the postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome: a case series. Dig Dis Sci 2013;58:3207-3211 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24068608/
- Elliot Overton, Sulfate IV: Chronic SIBO/Gut Dysbiosis As A Protective Adaptation To Supply Sulfate. July 21, 2018, Eonutrition.co.uk, https://www.eonutrition.co.uk/post/sulfate-iv-chronic-sibo-gut-dysbiosis-as-a-protective-adaptation-to-supply-sulfate
- Song C, Perides G, Wang D, Liu YF. beta-Amyloid peptide induces formation of actin stress fibers through p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Neurochem. 2002 Nov;83(4):828-36. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2002.01182.x. PMID: 12421354. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12421354/
- Frederic Dorandeu, Guilhem Calas, Gregory Dal Bo, Raafat Fares, Chapter 36 – Models of Chemically-Induced Acute Seizures and Epilepsy: Toxic Compounds and Drugs of Addiction, Editor(s): Asla Pitkänen, Paul S. Buckmaster, Aristea S. Galanopoulou, Solomon L. Moshé, Models of Seizures and Epilepsy (Second Edition),Academic Press, 2017, Pages 529-551, ISBN 9780128040669, https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-804066-9.00037-7. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780128040669000377 “Alterations of the neuronal cytoskeleton, and more precisely disruption of actin dynamics, seem then to contribute to changes in brain excitability, but the mechanisms leading to these changes remain still unresolved (Spence and Soderling, 2015).” Excerpt viewable in F-actin, ScienceDirect, https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/neuroscience/f-actin