Evidence of aging, five years on average, was found in survivors of Covid who experienced ongoing illness after an apparent recovery or even only ever having had mild symptoms initially. (1) Other research has found evidence of autoimmune antibodies against certain types of G-protein coupled receptors – need a different post for that.
- Evidence for Biological Age Acceleration and Telomere 2 Shortening in Covid-19 Survivors. Alessia Mongelli, Carlo Gaetano, Michela Gottardi Zamperla, et al., medRxiv, April 27, 2021, preprint, (1)
- “The results show a consistent biological age increase in the post-covid population (mean 58,44 DS 14,66 ChronoAge Vs. mean 67,18 DS 10,86 BioAge, P<0,0001), determining a DeltaAge acceleration of 10,45 DS 7,29 years (+5.25 years above range of normality) compared to 3,68 DS 8,17 years for the COVID19-free population (P<0,0001). A significant telomere shortening parallels this finding in the post-COVID19 cohort compared to COVID19-free subjects (post-COVID19 TL: 3,03 DS 2,39 Kb vs. COVID19-free: 10,67 DS 11,69 Kb; P<0,0001).” (1)
- Additionally, ACE2 expression was decreased in post-COVID19 patients compare to COVID19-free, while DPP-4 did not change. ” (1)
ACE2 receptor expression was expected to be decreased in patients with increased viral load due to the virus destroying the cells with the receptors. Eventually less ACE2 function would be left and patients would exhibit symptoms similar to genetic ACE2 knockout mice – bred to not have ACE 2 receptors in order to see the effect on health. It can provide information about what function something has to see what goes wrong when the animal doesn’t have it.
Also of interest – stopping the virus from entering the ACE2 receptor means that it can’t replicate and go on to infect other cells or people – pomegranate peel may block access: Pomegranate peel – anti-COVID19, may block ACE2 receptor access to the SARS-CoV-2 virus. I ate some pomegranate peel today. *Recipe at the end of this post, more information about pomegranate prep & benefits G13. Pomegranate.
Pomegranate extract reduces inflammation and modulates health and gene transcription.
Pomegranate extract, of the whole fruit or peel is a very potent anti-inflammatory and modulator of health, (6), even epigenetics to some extent – epigenetics effects which genes will be transcribed into proteins by the cell. Pomegranate extract was found to modulate/effect microRNAs which control which mRNA will get transcribed. (2)
“Pomegranate extract intake reversed the surgery-mediated upregulation of various miRNAs and mildly reduced expression of selected miRNAs in tumour tissue compared with normal tissue.” (2)
What is microRNA? — “Noncoding (nc) RNAs also possess a regulatory effect on gene expression. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small ncRNAs of 20–22 nt that inhibit gene expression at the posttranscriptional level either by imperfect base-pairing to the mRNA 3′-untranslated regions to repress protein synthesis, or by affecting mRNA stability (reviewed in [23]).” (2)
What is mRNA? — “Messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules carry the coding sequences for protein synthesis and are called transcripts;” (3) Messenger RNA is copied from the double helix strands of DNA that make a gene. The messenger RNA is a single helix – one ladder leg instead of both sides of the spiraling ladder with nucleotide steps, or one side of a zipper.
What is epigenetics? — “The term ‘epigenetics’ refers to modifications in gene expression caused by heritable, but potentially reversible, changes in DNA methylation and chromatin structure. Major epigenetic mechanisms include DNA hyper- and hypomethylation [11], remodelling of the chromatin, modification of histones by histone acetylation and methylation (among others), and noncoding RNAs [12].” (2)
What are methyl donors? — Folate in the bioactive methylated form and methylated B12 are both helpful for providing the methyl groups needed for DNA methylation. The small chemical group added onto genes is like turning the light switch off, that gene is no longer in the ready to be transcribed mode. Choline is another methyl donor in the B vitamin group. See: Methyl Donors & BPA.
EGCG found in Green tea & Pomegranate Peel may protect length of Telomeres.
Pomegranate peel is also a source of EGCG (more commonly associated with green tea) which has been found protective of telomere length, by inhibiting a telomerase enzyme.
“Epigallocatechin-3-gallate, a major component of green tea polyphenols, downregulated expression of human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT), a major enzyme determining telomere stability, through causing promoter hypomethylation and histone deacetylations, thereby inhibiting proliferation of breast cancer cells [12].” (7)
Polyphenols, alkaloids, triterpenes, and xanthones may be plant nutrients that help inhibit the overactivity of the telomerase enzyme seen in some types of cancer cells. (8) EGCG is a polyphenol. Alkaloids include “morphine, strychnine, atropine, colchicine, ephedrine, quinine, and nicotine.” (11) Triterpenes include sterols (such as vit. D group, 12) and carotenoids (vit A). (9) xanthones are found in the Garcinia, mangosteen fruit. (10) Telomeres are a section of non protein encoding DNA at the end of genes. Telomeres get shorter as we age and longer ones indicate younger metabolic age. Excessive lengthening of telomeres can occur in cancer and that isn’t good either.
The really good news about epigenetic changes – they can be changed back.
“In contrast to irreversible genetic alterations (mutations, deletions, etc.), genes silenced by epigenetic modifications are still intact and can be reactivated [13,14].” (2)
Many genes are turned on or off with the change from night to day/day to night. We do more active energy using work during the day, which produces waste chemicals, and more growth and repair, clean up, at night while we sleep. It is very unhealthy to chronically miss sleep.
Sunlight in the day & blackout curtains at night help immune function with melatonin & sunshine vitamins.
Sunlight in the morning or at some point in the awake hours of the day also helps health.
“People have a feeling of wellbeing when exposed to sunlight. This may be due to the fact that keratinocytes produce β-endorphin when exposed to UV radiation.67 ” (12)
A full spectrum lamp with UVB capability for a half hour of artificial “sun” during winter months or for night shift workers may be more beneficial for health, and mood, than a vitamin D2/D3 supplement. Our bodies make other forms of the vitamin D group of sterols, some water soluble, and other forms of vitamin A are also made. (12, 13)
“Bright light treatment requires a minimum of 2,500 lux to be effective, & the brightness recommended by researchers & clinicians for most people is 10,000 lux – an amount significantly higher than standard indoor lighting.” (14) This reference is recommending no UV in the light treatment, however for the vitamin D and A chemistry UVB is needed and UVA may also have some role in health in moderation.
Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) lamps may not provide the UVB, and the UVB intense ones are only meant for 30 minute use or less per day, as sunburn possible, so that type of light wouldn’t treat the SAD problem in the same way as the no UVB lights. (13, 15) The 10,000 lux lamps may be helping patients with Seasonal Affective Disorder (14) by increased beta-endorphins. Serotonin increase is involved in the benefit of Bright Light Therapy (BLT) which was found to be better than placebo in a metareview. (16) Bright Light Therapy was found to reduce cerebral monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) levels which have a seasonal decrease in healthy controls compared to participants with SAD. Serotonin receptors and transport proteins may also be affected by the light treatment. (17)
Black out curtains at night and covering all little alarm clock lights and other device lights helps our body switch into night-time biology of clean-up and repair. Melatonin is also made at night and lights can reduce the amount that is made. It helps immune function and seems helpful against COVID-19. Melatonin produced in the lungs prevents infection by novel coronavirus. (18)
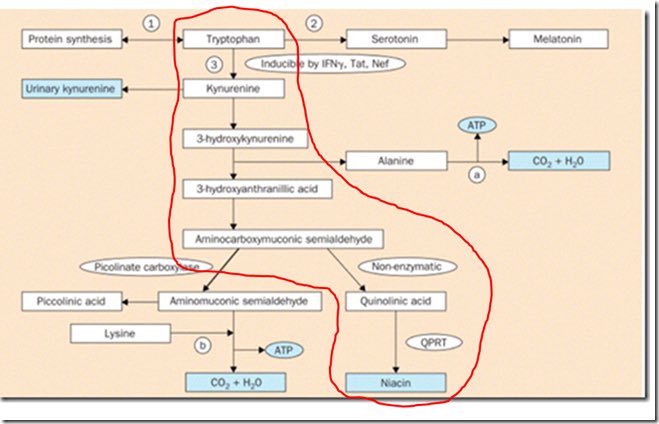
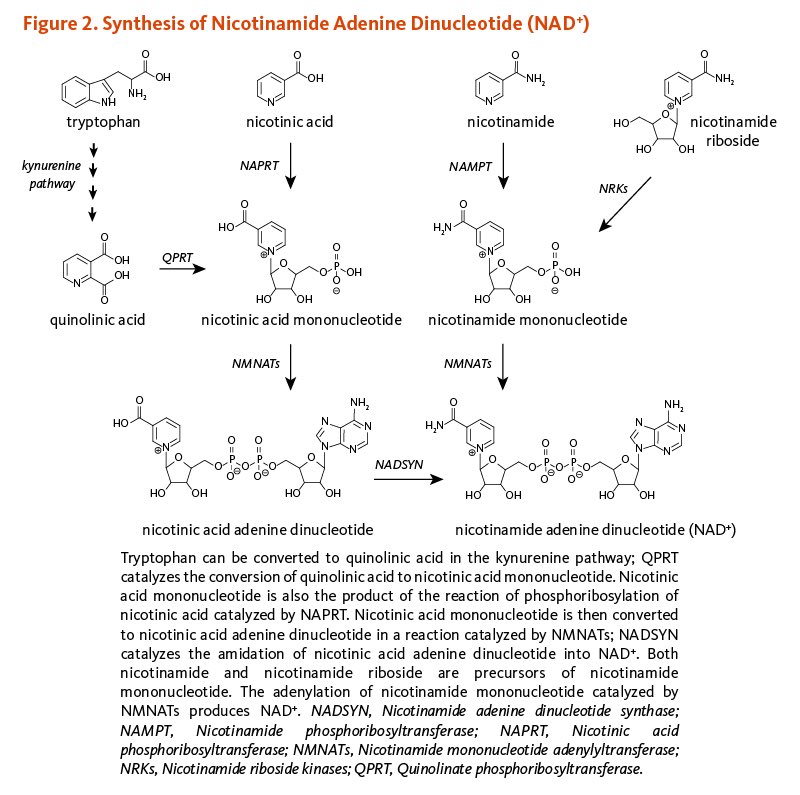
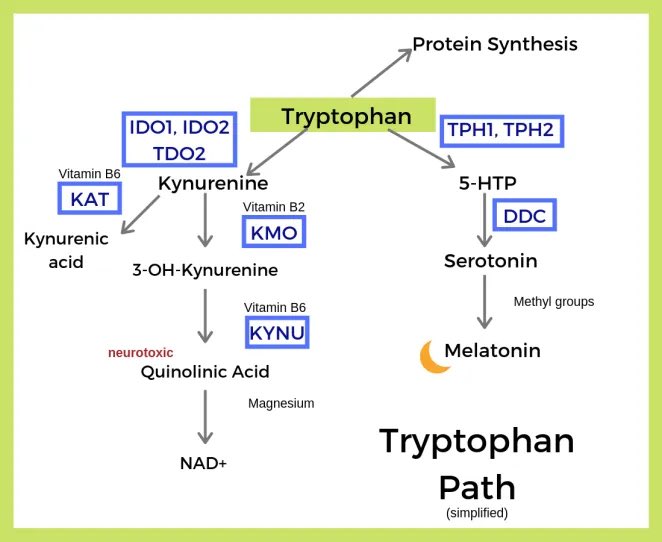
Lack of niacin, which is needed in increased amounts during infection or inflammation, would lead to overuse of tryptophan instead. Lack of tryptophan would lead to a lack of serotonin and melatonin, both of which are made from tryptophan. (19)
We may need a healthy gut microbiome, to have overall health.
The microbes in our intestines may have a larger role in health than we realized because they also impact our epigenetics – we want our good guys to be helping us then.
“Recent research has indicated that the gut microbiota and gut microbial metabolites might be important mediators of the diet–epigenome interaction (previously reviewed in [29–31]).” (2)
Obesity has been found to be related frequently to less beneficial microbiome species. (4) Anxiety can also be linked to microbiome species. (5) “Animal models strongly suggest a role for the gut microbiome in anxiety- and trauma-related disorders. The microbiota–gut–brain (MGB) axis sits at the epicenter of this new approach to mental health. The microbiome plays an important role in the programming of the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis early in life, and stress reactivity over the life span.” (5)
More information about POTS & epigenetic changes:
I go into more detail about epigenetic changes, methyl donors and Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS) – a problem that has been occurring for some Covid survivors and a problem I’ve had symptoms of twice and got better from twice – See: Epigenetic changes may also be involved in Covid19 or LongCovid. I prefer being healthy to being unhealthy and I’m willing to work to get better when I can.
Seasoned Peas and Pistachios, with Pomegranate peel.
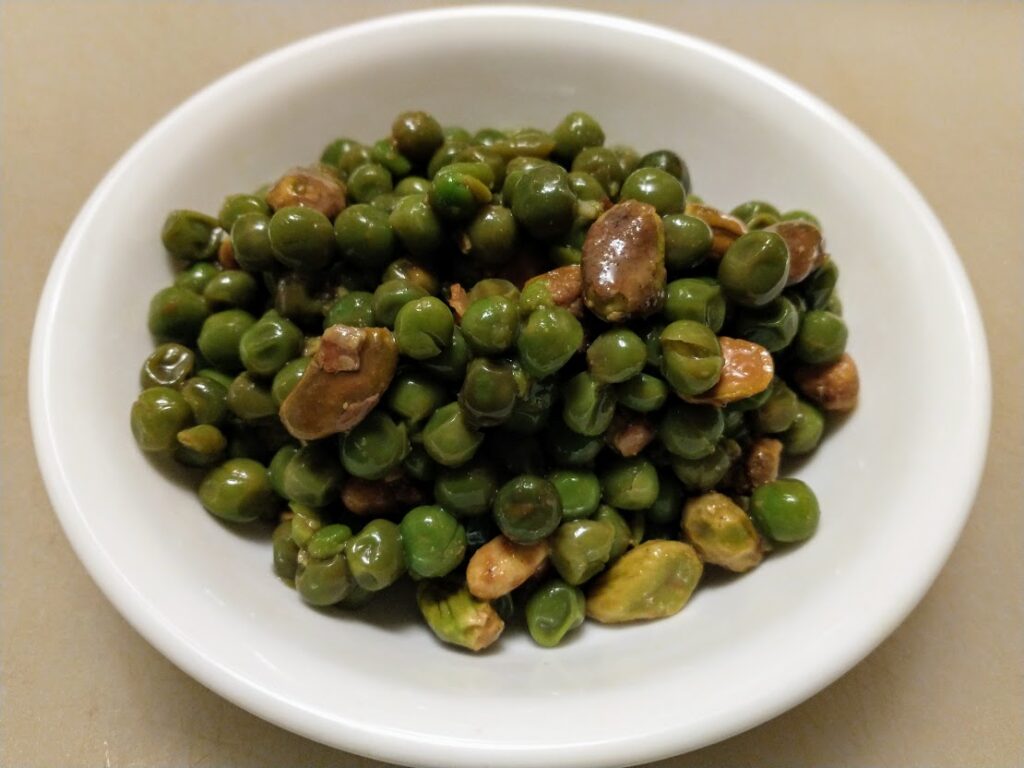

*Pound of frozen Peas, boil for a few minutes with a cup of Pistachios in water to cover the food – then pour off the water. It may contain oxalates from the pistachios. Add a 1/4 cup of fresh water to the drained food along with a half teaspoon of Cumin, Coriander and Gumbo file; one tablespoon powdered or minced dehydrated Pomegranate Peel (inner pith); and simmer with the peas & pistachios for a minute or two to set the Gumbo file thickener and mix the flavors. Serve the peas hot or cold with a little Apple Cider Vinegar and Salt to taste. Makes about four 3/4 cup servings.
Disclaimer: Opinions are my own and the information is provided for educational purposes within the guidelines of fair use. While I am a Registered Dietitian this information is not intended to provide individual health guidance. Please see a health professional for individual health care purposes.
Reference List
- Alessia Mongelli, Carlo Gaetano, Michela Gottardi Zamperla, et al., Evidence for Biological Age Acceleration and Telomere 2 Shortening in Covid-19 Survivors. medRxiv, April 27, 2021, preprint, https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.04.23.21255973v1
- Clarissa Gerhauser, Impact of dietary gut microbial metabolites on the epigenome. Royal Society, 23 April 2018, https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2017.0359 https://royalsocietypublishing.org/doi/10.1098/rstb.2017.0359
- Ribosomes, Transcription, and Translation, nature.com/scitable https://www.nature.com/scitable/topicpage/ribosomes-transcription-and-translation-14120660/
- Davis CD. The Gut Microbiome and Its Role in Obesity. Nutr Today. 2016;51(4):167-174. doi:10.1097/NT.0000000000000167 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5082693/
- Stefanie Malan-Muller, Mireia Valles-Colomer, Jeroen Raes, et al., The Gut Microbiome and Mental Health: Implications for Anxiety- and Trauma-Related Disorders. OMICS J of Integ Biology, Vol 22, 2, 2018, Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. DOI: 10.1089/omi.2017.007 https://www.liebertpub.com/doi/pdfplus/10.1089/omi.2017.0077
- Ceci C, Lacal PM, Tentori L, De Martino MG, Miano R, Graziani G. Experimental Evidence of the Antitumor, Antimetastatic and Antiangiogenic Activity of Ellagic Acid. Nutrients. 2018;10(11):1756. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6266224/Published 2018 Nov 14. doi:10.3390/nu10111756
- Yan Bian, Juntong Wei, Changsheng Zhao and Guorong Li, Natural Polyphenols Targeting Senescence: A Novel Prevention and Therapy Strategy for Cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2020, 21, 684; https://www.dropbox.com/s/wckq66cgye3yjr4/ijms-21-00684-v3.pdf?dl=0doi:10.3390/ijms21020684
- Kumar Ganesan ID and Baojun Xu, Telomerase Inhibitors from Natural Products and Their Anticancer Potential. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 13; doi:10.3390/ijms19010013 https://www.dropbox.com/s/xjhguj3dnbop6h2/ijms-19-00013.pdf?dl=0
- Triterpenes, sciencedirect.com, https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/chemistry/triterpene
- Xanthones, sciencedirect.com, https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/agricultural-and-biological-sciences/xanthone
- Alkaloids, sciencedirect.com, https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/food-science/alkaloid
- Wacker M, Holick MF. Sunlight and Vitamin D: A global perspective for health. Dermatoendocrinol. 2013;5(1):51-108. doi:10.4161/derm.24494 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3897598/
- CK Eternity, The Truth about Vitamin D Metabolism, Mar 12, 2021, Patreon.com, https://www.patreon.com/posts/truth-about-d-48683534
- Bright Light Treatment Research. sunbox.com, https://www.sunbox.com/research/bright-light-treatment-research/
- Ezvid Wiki, The 6 Best Vitamin D Lights – 2019, Nov 28, 2018, youtube.com, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iqk9hzYC5Mc&feature=youtu.be
- Pjrek E, Friedrich M, -E, Cambioli L, Dold M, Jäger F, Komorowski A, Lanzenberger R, Kasper S, Winkler D: The Efficacy of Light Therapy in the Treatment of Seasonal Affective Disorder: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Psychother Psychosom 2020;89:17-24. doi: 10.1159/000502891 https://www.karger.com/Article/Abstract/502891
- Spies, M., James, G.M., Vraka, C. et al. Brain monoamine oxidase A in seasonal affective disorder and treatment with bright light therapy. Transl Psychiatry8, 198 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-018-0227-2 https://www.nature.com/articles/s41398-018-0227-2
- Elton Alisson, Melatonin produced in the lungs prevents infection by novel coronavirus. Agência FAPESP, Jan 27, 2021 https://www.eurekalert.org/pub_releases/2021-01/fda-mpi012721.php
- Dmitry Kats, Tweets & images regarding tryptophan, melatonin, and niacin. “Yes, and melatonin is depleting as a result of tryptophan depleting due to inflammation, and only exclusively sufficient niacin supply can flush this inflammation out to then accordingly restore auxiliary biochem and health” “Funny how melatonin is being pushed through publications in relation to #COVID19, whilst they purposefully censor or “ignore” the inflammatory biochemical mechanism that causes this melatonin deficiency & how sufficient niacin supply nips the inflammation in the bud to restore it” https://twitter.com/NiacinIsHealth/status/1354624867300241408?s=20